Testosterone serves as a vital hormone within the male physiology, orchestrating diverse functions including the development of muscle mass, preservation of bone density, regulation of libido, and stabilization of mood. This hormone is central to defining male characteristics and supporting general wellness. Nevertheless, the concentration of testosterone can shift considerably throughout a man’s life, primarily influenced by the aging process.
This detailed report examines the typical testosterone levels experienced by men across different age brackets, investigating the natural transformations that occur as they mature. We utilize data and perspectives from established publications, such as HealthGains, Healthline, and Medichecks, to offer a thorough description of the average testosterone levels in men relative to their age.
Defining Normal Testosterone Concentrations
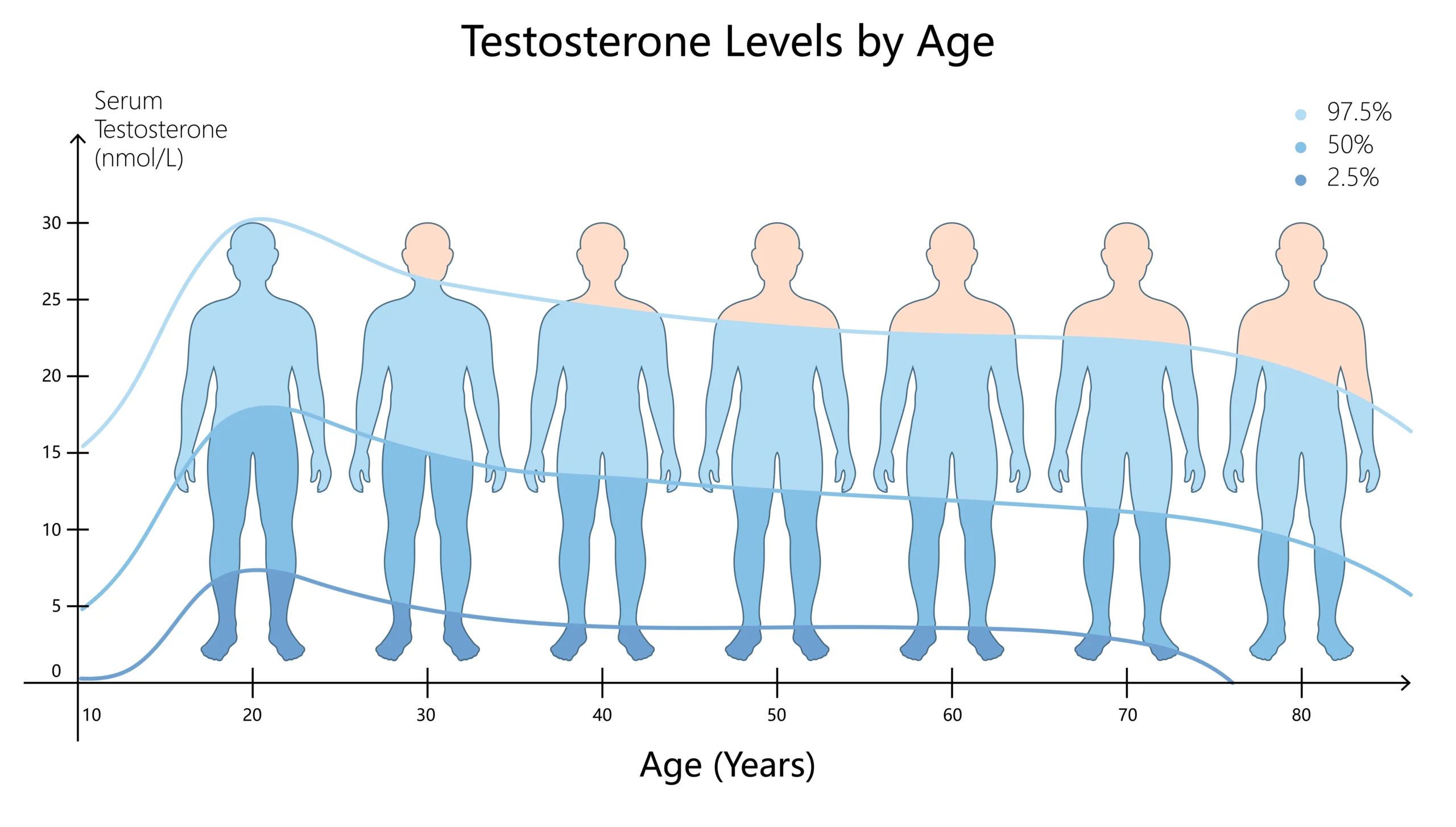
Prior to exploring the statistics related to specific age groups, it is crucial to establish the parameters of a healthy testosterone concentration and the method used for its quantification. Testosterone concentration is usually quantified in nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL) within the bloodstream. While the acceptable range for mature men fluctuates, it commonly spans from 270 up to 1070 ng/dL.
It must be acknowledged that testosterone measurements differ significantly among individuals, being susceptible to influences from factors like heredity, daily habits, and pre-existing medical issues. A level deemed “standard” for one person might be atypical for someone else. Nevertheless, analyzing the mean testosterone levels corresponding to age provides valuable insight into the anticipated hormonal evolution across the male lifespan.
Testosterone Concentrations During Puberty
The adolescent phase signals the initiation of profound endocrine shifts in young males as they move from youth toward maturity. At this time, the body undergoes a rapid increase in testosterone synthesis, which triggers the emergence of secondary male traits, including the growth of facial hair, vocal deepening, and enhanced muscle volume.
Based on the referenced sources, the typical testosterone measurements for male adolescents generally fall within the range of 300 to 1,000 ng/dL. Nonetheless, personalized differences can be considerable throughout this stage, meaning some boys may register readings above or below this spectrum. It is necessary to remember that these figures are estimates and are subject to individual variation.
Testosterone Concentrations in Early Adulthood

During the early adult years, testosterone concentrations are sustained at an elevated rate. This time frame usually corresponds to a man’s highest point of physical capability and sexual function. Generally, males in their twenties and thirties exhibit testosterone levels between 270 and 1070 ng/dL.
In this life stage, testosterone aids in promoting muscle development, maintaining high energy, and supporting general vigor. Males commonly possess strong physical power and a healthy sex drive. It should be noted, though, that personal habits, including nutritional choices, physical activity, and handling stress, can impact testosterone concentrations even when men are young.
Testosterone Concentrations During Midlife
When men reach their fourth and fifth decades (40s and 50s), the concentration of testosterone typically begins a slow reduction. This phenomenon is an inherent aspect of maturation, often termed “andropause” or the “male climacteric.” Data from the HealthGains article indicates that the mean testosterone levels for men aged 40 to 49 usually fall between 252 and 916 ng/dL, whereas those aged 50 to 59 may show ranges from 215 to 878 ng/dL.
This decrease in testosterone during midlife can manifest through several indicators, such as diminished sexual desire, loss of muscle bulk, persistent tiredness, and emotional instability. Nonetheless, it is vital to stress that not every man will suffer from pronounced symptoms, and the intensity of these effects differs considerably among individuals.
Testosterone Concentrations in Advanced Age
As the male lifespan progresses, testosterone concentrations persistently decrease. Once men enter their sixties and seventies, the typical readings are likely to drop even lower. The Medichecks publication suggests that males who are 60 years of age and above generally exhibit testosterone levels spanning from 192 to 916 ng/dL.
Reduced testosterone concentrations in later life may contribute to numerous health concerns, such as diminished bone mineral density, atrophy of muscle tissue, and an elevated vulnerability to osteoporosis. Furthermore, these lower levels might negatively affect mental processing and emotional state, potentially resulting in symptoms like melancholy and impaired focus.
The Health Consequences of Insufficient Testosterone
A deficiency in testosterone, medically termed hypogonadism, carries profound health consequences regardless of a man’s age. Although a gradual reduction due to aging is expected, concentrations that are pathologically low can give rise to a multitude of medical disorders.
- Diminished Muscle Volume and Power: Insufficient testosterone can cause muscle wasting (atrophy) and lessen physical capability, thereby hindering mobility and overall life satisfaction.
- Elevated Tiredness: Persistent weariness and lowered energy are frequent indicators of testosterone deficiency, negatively affecting daily routines and output.
- Impaired Sexual Desire and Erectile Issues: Given testosterone’s essential role in sexual performance, a reduction in the hormone often results in lessened libido and difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Emotional Instability: Low testosterone concentrations are connected to heightened irritability, rapid shifts in mood, and a greater predisposition toward depressive states.
- Reduced Skeletal Mass: Since testosterone assists in preserving bone density, a deficit can heighten the danger of fractures and osteoporosis, particularly for older individuals.
- Mental Clarity: Certain studies propose a link between low testosterone and impaired cognitive processing, potentially increasing the likelihood of mental decline in aging males.
- Heart and Vascular Wellness: Low testosterone levels have been correlated with an elevated threat of cardiovascular ailments, such as stroke and coronary artery disease.
It should be noted that although a testosterone deficit may exacerbate these medical concerns, it is rarely the singular trigger. A person’s overall wellness is also significantly influenced by other variables, including nutrition, physical activity, genetic predisposition, and coexisting health problems.
Therapeutic Approaches for Testosterone Deficiency
When a male exhibits signs of testosterone deficiency and consults a physician, several therapeutic avenues can be pursued. A medical professional must evaluate the patient’s unique requirements and potential risks when determining these options. Typical interventions encompass:
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): This therapeutic approach involves administering testosterone via methods such as injections, topical gels, skin patches, or subcutaneous implants. TRT is effective in mitigating deficiency symptoms and enhancing general quality of life.
- Modifying Daily Habits: Implementing constructive lifestyle adjustments, such as consistent physical activity, consuming a nutritious diet, effective stress control, and sufficient rest, can naturally aid in maximizing testosterone production.
- Optimal Body Weight: Sustaining a healthy weight is beneficial for preserving ideal testosterone concentrations, as excessive body fat is frequently correlated with reduced levels.
- Managing Root Causes: It is crucial for holistic health to resolve any existing medical issues that might be contributing to the testosterone deficit, such as diabetes or excessive weight.
- Pharmaceutical Interventions: Certain pharmacological agents may be recommended in specific scenarios to encourage the body’s own testosterone synthesis or to treat specific related symptoms.
For those individuals noticing indicators of insufficient testosterone, seeking consultation with a healthcare professional is mandatory to establish the best and safest plan of care.
Summary of Age-Specific Testosterone Levels
Grasping the typical testosterone concentrations relative to a man’s age is fundamental knowledge for patients and clinicians alike. Although a natural reduction in the hormone occurs as one ages, marked differences persist between individuals. By upholding a healthy regimen, engaging in consistent physical activity, and ensuring adequate nourishment, men can support optimal testosterone readings and general vitality across their lifespan.
It is vital to monitor testosterone levels and intervene promptly when deficiencies are identified, thereby reducing the severity of associated symptoms and ensuring a sustained high quality of life. Through awareness of their hormonal status and accessing professional medical support, men are better equipped to manage age-related endocrine shifts while preserving peak health and vigor.
Read also: Do Cold Showers Increase Testosterone?